Webots Collision Avoidance
WEBOTS BUG1 & BUG2 Display
Overview
Using a wheeled robot Pioneer 3-DX. A display of BUG1 and BUG2 Algorithms showcase how the wee robot and reach it’s destination including whilst avoiding obstacles. No Fancy AI🧠 was used just simple maths📏
Here is the equation for the bug algorithm distance
Wall-Following Algorithm
To follow a wall without crashing, I use a Proportional–Integral–Derivative (PID) controller, as while following the wall, I may travel closer or further than expected. PID controllers are a good way to correct but not overcorrect any error. To get the performance I currently have, I had to experiment with parameter values.
Experimentation and Results
Bug 1 Results

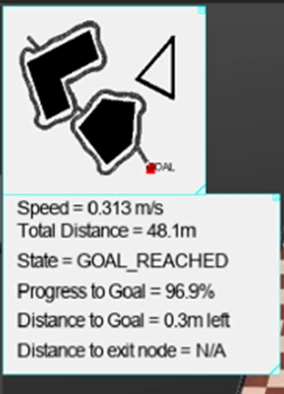
Total Distance = 48.1m
Bug2 Results
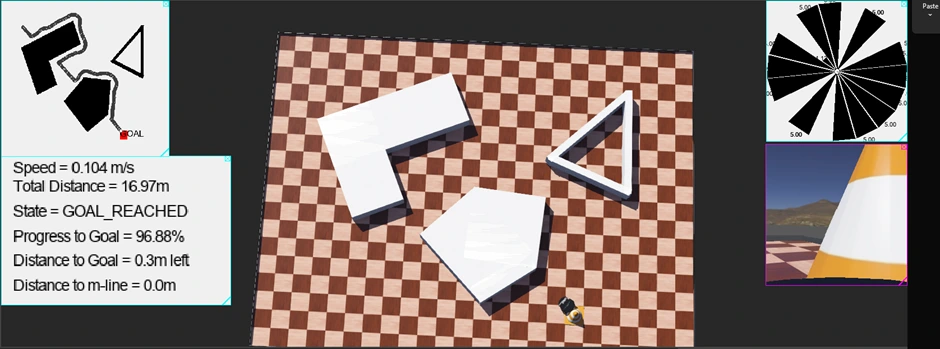
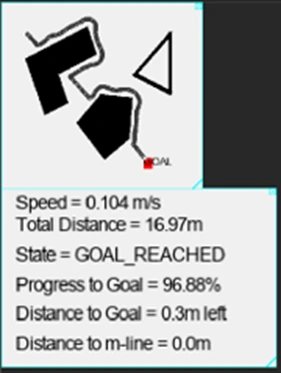
Total Distance = 16.97m
Bug2 Results performed significantly better than Bug1's. Bug2 travelled much less distance as seen by the mini-map and total distance. Also not shown but calculated, Bug2 found the goal in a much faster time than Bug1.
In addition, Bug1, although simplistic in nature, was more complex to code due to more states being involved than Bug2.
Challenges and Reflections
Challenges:
- PID controller
- The controller took a long time to fine-tune to a stable state through experimenting with parameters. But by tuning P-D-I parameters in that order, I found a stable state. For future iterations, I wish this PID controller to perform better and smoother.
EventHandler- Turning the system from synchronous-based to asynchronous was challenging, especially considering Java is a strongly typed language. Creating custom definitions for the event handler was cumbersome.
- Turning corners without over/under shooting
- While experimenting with the bot, I over/undershot the corner many times, either hitting the incoming wall head-on or undershooting in open space. To fix this, I found using the back-side sensors (S15 & S8) to skew bot perception of side wall, so I turned those sensors off and only use S0 & S7.
Reflections:
- Better turning
- The robot will stop and turn. In the future, I wish it to arc on a smooth curve to desired position, without under/overshooting like my previous attempts.
- More Efficient approach
- Currently, I believe every timestep the bot is processing too many things at a given time, and the execution of the Bug1 and Bug2 Algorithm could be better. For example, with Bug1, I don't need to check every time if there is a new shortest exit pose. Solving these inefficiencies would allow for smaller embedded systems to run easier.
Conclusion
To conclude the assignment, I believe it went well, hitting many of the marks set: being able to have a successful wall-following algorithm, implement both Bug1 and Bug2 algorithms, and code and comment using best practices. The Bug2 algorithms outperform Bug1's, and there can only be a few specific layouts where Bug1 beats Bug2. However, I should mention that other algorithms and implementations can perform better than these bug algorithms; however, they do require additional data such as a map and greater sensor data.
CODE EXPLANATION
Event Handler
Is responsible for storing, manipulating, and initiating the robot actions/events like the action to wall follow or move straight. It stores events in a stack-like structure, executing events on top of the stack each iteration.
The EventHandler class is needed because of the asynchronous nature of the Bug1 and Bug2 algorithms. As the bot operates in an uncertain, unknown world, it needs to be able to react and adapt to the outside world in real time. Making an event handler that was purely synchronous/based on time thus would not be possible as the bot would need to know details of its local domain, which is impossible to do without mapping or hardcoding. Asynchronous behaviour is perfect for helping in executing the bug algorithms as it allows the robot's behavior to change according to the sensor reading/outside world. For example, commands like "Keep going straight until a wall is reached" is now doable. However, EventHandler can perform timed events if needed.
PioneerNav2
This class is wholly responsible for the bot's movement. Using differential drive logic and mathematics, this class manages to move the robot in all directions of the 2-D plane, including arching.
PioneerProxSensors1
This class is responsible for making and interpreting sonar sensor data, allowing the bot to know if an object is nearby, from which direction, and how far.
BaseDisplay & MapDisplay & DataDisplay & Obstacle
These classes deal with displaying information to the display. DataDisplay, MapDisplay, and PioneerProxSensors1 all extend from BaseDisplay. The Obstacle Class represents each obstacle and goal object on the mini-map.
BaseBugAlgorithm
Contains most of the logic that will be used for both classes. Both Bug1 and Bug2 contain many similarities in execution; for example, both algorithms:
- Pivot to goal and move forward in a straight line to it, at the start.
- Both will react when an obstacle is observed.
- Wall follow
- Need to pivot to goal several times.
- Need to terminate execution once goal is reached.
/**
* BaseBugAlgorthim is the base class for bug algorithms, not abstract to allow Type conversions
*/
public class BaseBugAlgorthim {
protected final Pose goalPose;
protected Pose robotPose;
protected final EventHandler eventHandler;
protected final double robotVelocity;
protected final PioneerNav2 nav;
protected Pose entryPose; // bug 1 issue// could be used for bug 2
protected boolean circlingObject = false;
protected int targetTime = 5000;
protected double timeElapsed = 0;
protected boolean hasTimeElapsed = false;
/**
* Constructor for BaseBugAlgorthim
*
* @param goalPose GOAL POSE
* @param robotPose Robot Pose
* @param robotVelocity Robot Velocity
* @param nav PioneerNav2
* @param eventHandler EventHandler
*/
public BaseBugAlgorthim(Pose goalPose, Pose robotPose, double robotVelocity, PioneerNav2 nav,
EventHandler eventHandler) {
this.goalPose = goalPose;
this.robotPose = robotPose;
this.robotVelocity = robotVelocity;
this.nav = nav;
this.eventHandler = eventHandler;
this.moveToGoal();
}
/**
* Increments the distance data
*/
protected void incrementDistanceData() {
Utils.incrementDistance(robotPose, 32);
}
/**
* Updates the robot pose
*/
protected void updateRobotPose() {
this.robotPose = nav.getRealPose();
}
/**
* Updates the time elapsed
*/
public void updateTime() {
if (!hasTimeElapsed) {
this.timeElapsed += 32;
}
if (targetTime < this.timeElapsed) {
this.hasTimeElapsed = true;
}
}
/**
* Moves the robot to the goal
*/
protected void moveToGoal() {
this.circlingObject = false;
double angleToGoal = Utils.angleToGoal(nav.getRealPose(), goalPose);
boolean clockwise = angleToGoal > 0;
EventInterface rotateEvent = new EventInterface(
EventHandler.Event.ARC,
new Object[] { angleToGoal, 0.0, robotVelocity, !clockwise },
true);
EventInterface moveForwardEvent = new EventInterface(
EventHandler.Event.FORWARD,
new Object[] { 1.0, robotVelocity },
false);
eventHandler.addCurrEvent(moveForwardEvent);
eventHandler.addCurrEvent(rotateEvent);
}
/**
* Runs the bug algorithm, only here in superclass for polymorphism
*/
public void run() {
};
/**
* Returns the distance to exit, also here for polymorphism
*
* @return distance to exit
*/
public double distanceToExit() {
return 0;
}
/**
* Begins wall following
*/
protected void beginWallFollow() {
this.circlingObject = true;
int wall = nav.isWall(Constants.SETPOINT_THRESHOLD + 0.1);
if (wall != 0) {
Object[] eventParameters = wall == 1 ? new Object[] { robotVelocity, Constants.SETPOINT_THRESHOLD, true }
: new Object[] { robotVelocity, Constants.SETPOINT_THRESHOLD, false };
EventHandler.Event interfaceEvent = wall == 1 ? EventHandler.Event.WALL_FOLLOW_RIGHT
: EventHandler.Event.WALL_FOLLOW_LEFT;
EventInterface wallFollowEvent = new EventInterface(interfaceEvent, eventParameters, false);
EventHandler.Event event = eventHandler.getCurrEvent().getEvent();
if (event == EventHandler.Event.WALL_FOLLOW_LEFT || event == EventHandler.Event.WALL_FOLLOW_RIGHT) {
// if already wall following, do nothing
} else {
eventHandler.addCurrEvent(wallFollowEvent);
}
}
}
/**
* Checks if the robot has reached the pose
*
* @param pose Pose
* @return true if reached pose
*/
protected boolean hasReachedPose(Pose pose) {
return Utils.getDistance(robotPose, pose) < 0.3;
}
/**
* Checks if the robot has reached the goal
*
* @return true if reached goal
*/
protected boolean isGoalReached() {
if (Utils.getDistance(robotPose, goalPose) < 0.3) {
EventInterface stopEvent = new EventInterface(
EventHandler.Event.GOAL_REACHED,
new Object[] {},
false);
eventHandler.replaceCurrEvent(stopEvent);
System.out.println("Goal Reached");
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
/**
* Detects wall and begins wall following
*/
protected void detectWall() {
if (!this.circlingObject && nav.isWall(0.30) != 0) {
this.entryPose = robotPose;
this.beginWallFollow();
}
}
/**
* Detects if the robot has left the wall
*/
protected void leaveWall() {
if (this.circlingObject && nav.isWall(0.30) == 0) {
this.circlingObject = false;
this.entryPose = null;
this.moveToGoal();
}
}
/**
* Resets the robot and moves to goal
*/
protected void resetAndMoveToGoal() {
this.timeElapsed = 0;
this.hasTimeElapsed = false;
this.circlingObject = false;
this.entryPose = null;
this.moveToGoal();
}
}
Bug1 extends BaseBugAlgorithm
The Bug1 class makes the bot pivot to goal and move in a straight line towards it. If a wall is detected, it begins wall following and records the pose of entry point to wall following. While wall following, Bug1 at intervals will record current pose and current distance to goal and will continue to do so until the obstacle is circled/entry point is reached again. At this point, it will know the pose around the wall with the shortest exit point to goal. The bot will re-circle to that pose and exit the wall, pivoting in a straight line to the goal. These sets of actions repeat until the goal is reached.
/**
* Bug1 algorithm
*/
public class Bug1 extends BaseBugAlgorthim {
private double shortestExistDistance = Double.MAX_VALUE;
private Pose exitPose;
private boolean isCircled = false;
private int targetTime = 5000;
private double timeElapsed = 0;
/**
* Constructor for Bug1
*
* @param goalPose GOAL POSE
* @param robotPose Robot Pose
* @param robotVelocity Robot Velocity
* @param nav PioneerNav2
* @param eventHandler EventHandler
*/
public Bug1(Pose goalPose, Pose robotPose, double robotVelocity, PioneerNav2 nav, EventHandler eventHandler) {
super(goalPose, robotPose, robotVelocity, nav, eventHandler);
}
/**
* Every Pose update when, checks current pose if shortest is shortest distance.
*/
private void recordShortestDistance() {
if (shortestExistDistance > Utils.getDistance(nav.getRealPose(), goalPose)) {
shortestExistDistance = Utils.getDistance(nav.getRealPose(), goalPose);
exitPose = nav.getRealPose();
}
}
/**
* Resets the robot and moves to goal
*/
private boolean circledToEntryPose() {
return this.hasReachedPose(entryPose);
}
/**
* Resets the robot and moves to goal
*/
private boolean hasReachedExsitPose() {
if (exitPose == null) {
return false;
}
return this.hasReachedPose(exitPose);
}
/**
* Resets the robot and moves to goal
*/
public void run() {
this.incrementDistanceData();
if (this.circlingObject) {
this.updateTime();
}
this.updateRobotPose();
this.detectWall(); // detect wall and auto begins to circle if wall detected
if (this.circlingObject) {
if (!this.isCircled) {
// record shortest exist distance
// continue to wall follow
if (this.circledToEntryPose() && this.hasTimeElapsed) {
System.out.println("Circled to entry pose");
this.isCircled = true;
return;
// continue to wall follow
}
this.recordShortestDistance();
return;
} else {
if (this.hasReachedExsitPose()) {
// reset and exist
this.resetAndMoveToGoal();
this.isCircled = false;
this.shortestExistDistance = Double.MAX_VALUE;
this.exitPose = null;
}
// if not reached exist pose
// continue to wall follow
}
}
this.isGoalReached();
}
public double distanceToExit() {
if (this.exitPose == null || !this.isCircled) {
return -1;
}
return Utils.getDistance(robotPose, this.exitPose);
}
}
Bug2 extends BaseBugAlgorithm
At instantiation, Bug2, using the Pythagorean theorem, will create a linear equation from current pose to goal pose using the LinearEquation class. From there, Bug2 will continue in parallel with the linear equation until an obstacle has been reached. Then it will wall follow around the obstacle until it has reached the location where the linear equation would lie. It does this by calculating given its current pose. If the robot is on its coordinate, then it knows to exit the obstacle and continue in a straight line along the linear equation line to goal. This process is repeated until the goal is reached.
/**
* bug2 algorithm extends BaseBugAlgorithm
*/
public class Bug2 extends BaseBugAlgorthim {
private final LinearEquation line;
/**
* Constructor for Bug2
*
* @param goalPose GOAL POSE
* @param robotPose Robot Pose
* @param robotVelocity Robot Velocity
* @param nav PioneerNav2
* @param eventHandler EventHandler
*/
public Bug2(Pose goalPose, Pose robotPose, double robotVelocity, PioneerNav2 nav, EventHandler eventHandler) {
super(goalPose, robotPose, robotVelocity, nav, eventHandler);
this.line = new LinearEquation(robotPose, goalPose);
}
/**
* Runs the bug2 algorithm and updates the robot pose
*/
public void run() {
this.isGoalReached();
this.incrementDistanceData();
if (this.circlingObject) {
this.updateTime();
}
this.updateRobotPose();
this.detectWall(); // detect wall and auto begins to circle if wall detected
if (this.circlingObject && this.hasTimeElapsed) {
double distanceToExit = this.distanceToExit();
if (distanceToExit < 0.15) {
this.resetAndMoveToGoal();
return;
}
}
}
/**
* Returns the distance to the exit based on m-line
*
* @return distance to exit
*/
public double distanceToExit() {
Pose exitPose = line.findPoseBasedOnX(nav.getRealPose());
double distanceToExit = Utils.getDistance(nav.getRealPose(), exitPose);
return distanceToExit;
}
}